Do you like milk on your cornflakes in the morning, or a nice glass of milk with your dinner? Not only is milk refreshing and great tasting, but it is also full of energy and protein that helps us grow and keeps our muscles, teeth and bones strong and healthy?
Many of you might live on farms where milk is produced, called dairy farms. There are over 17,000 dairy farms in Ireland, and there are almost 1.5 million dairy cows living on these farms. Now, we can’t drink all that milk in Ireland, so it is used to make lots of tasty things like ice cream and chocolate and cheese. Some is even turned into drinks like Baileys that your Mam and Dad might drink.
However, most of the milk we use in Ireland is dried and converted to a product called milk powder. When milk is converted to milk powder, it can be stored for a long time and transported all over the world.
In Ireland we grow a lot of grass, and we use this to feed to cows and sheep. So, farmers try to match the amount of grass they grow on their farms to the needs of their cows. Now you all know that grass grows really well in the spring and summer time (you probably have to help Mam and Dad mow the lawn then) but grass doesn’t grow so well in the winter. During the winter the cows go into the sheds and are fed silage.

\ Donal O' Leary
Dairy farmers will usually organise for their cows to calve in February and March, so there is lots of grass growing all summer to help the cows produce all that milk. Ireland is pretty special in the way we produce milk as most countries around the world don’t have the same opportunity to grow grass like we do.
Drying off
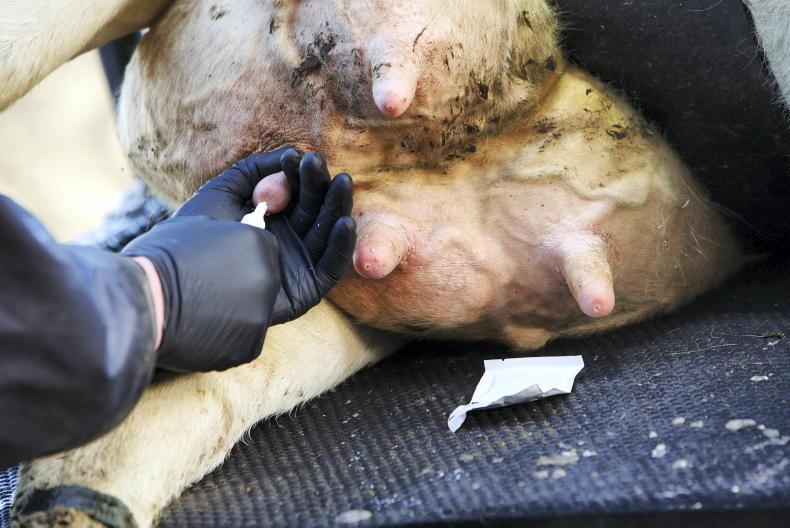
Less grass also means that we are getting to the time of the year when many cows are coming to the end of their milk production for the year. Over the next six weeks a lot of the cows in the country will have a break from milk production or will be ‘dried-off’. This is when the farmer stops milking the cows. It is the same as what happens on suckler farms when the calf is removed from the cow or weaned.
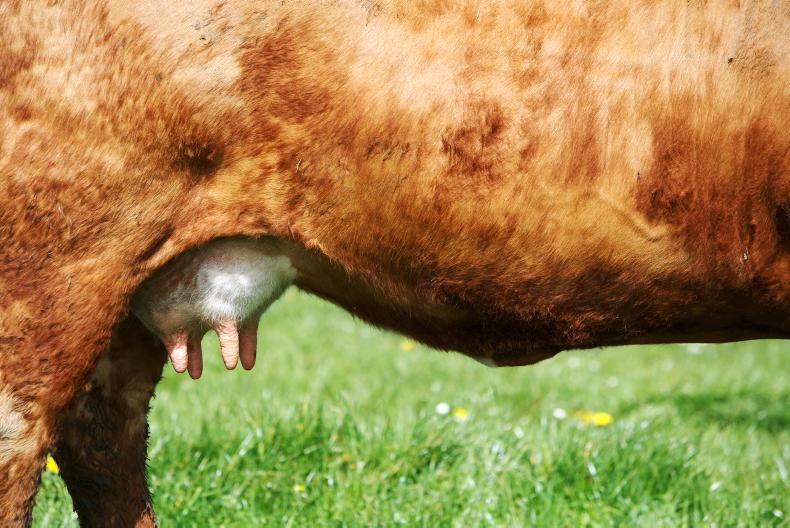
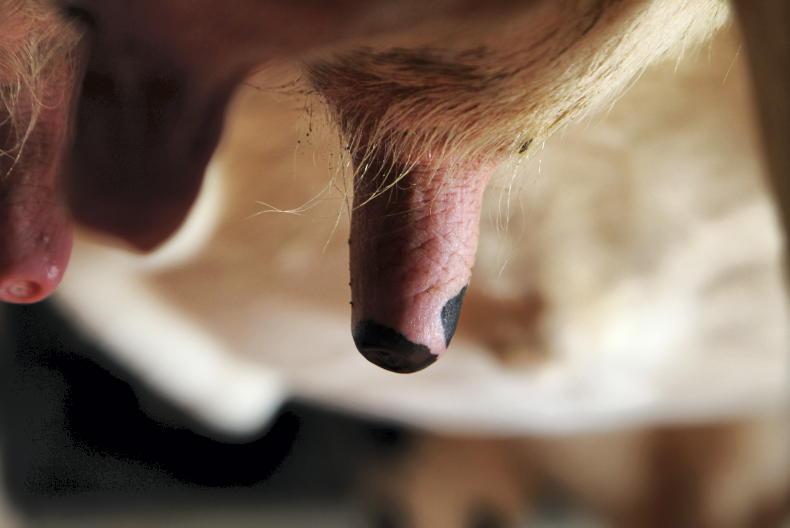
This is really important as it gives the ‘mammary gland’ the special organ which produces the milk, a chance to rest and repair, before the new calf is born, and the cow begins to produce milk again. The mammary gland is a really cool organ, and it has lots of different names around the country. Some people call it the udder, and others the elder and lots of other names too.
When the cow eats grass and other feeds, the bugs in their stomachs and some special chemicals called enzymes are used to break down that grass and then the cow takes the good parts like amino acids, and energy and fatty acids and minerals and use these to produce milk and help the cow to stay healthy. These nutrients travel around the body in the bloodstream, and when they reach the liver, they are directed to where they are most needed. When the cow is producing milk, a lot of these nutrients are needed in the mammary gland, so that is where the liver sends them. When they arrive at the mammary gland, some of these nutrients are transferred directly into the milk, but others are used to make bigger, more complicated parts of the milk, by special cells in the mammary gland, called secretory cells.
On most farms the cows are milked twice per day. The first milking happens in the morning time, sometimes very early, and then again in the evening. Dairy farmers must milk their cows twice a day, every day, so it is hard work. That’s why lots of dairy farmers really look forward to the break they get when the cows are dried off. But some dairy farmers milk cows all year round (not the same cows for the entire year) and this is where the fresh milk comes from for your breakfast every day!
Read more
Demand and points rise for agricultural science courses
Getting to know the basics of cereals
Do you like milk on your cornflakes in the morning, or a nice glass of milk with your dinner? Not only is milk refreshing and great tasting, but it is also full of energy and protein that helps us grow and keeps our muscles, teeth and bones strong and healthy?
Many of you might live on farms where milk is produced, called dairy farms. There are over 17,000 dairy farms in Ireland, and there are almost 1.5 million dairy cows living on these farms. Now, we can’t drink all that milk in Ireland, so it is used to make lots of tasty things like ice cream and chocolate and cheese. Some is even turned into drinks like Baileys that your Mam and Dad might drink.
However, most of the milk we use in Ireland is dried and converted to a product called milk powder. When milk is converted to milk powder, it can be stored for a long time and transported all over the world.
In Ireland we grow a lot of grass, and we use this to feed to cows and sheep. So, farmers try to match the amount of grass they grow on their farms to the needs of their cows. Now you all know that grass grows really well in the spring and summer time (you probably have to help Mam and Dad mow the lawn then) but grass doesn’t grow so well in the winter. During the winter the cows go into the sheds and are fed silage.

\ Donal O' Leary
Dairy farmers will usually organise for their cows to calve in February and March, so there is lots of grass growing all summer to help the cows produce all that milk. Ireland is pretty special in the way we produce milk as most countries around the world don’t have the same opportunity to grow grass like we do.
Drying off
Less grass also means that we are getting to the time of the year when many cows are coming to the end of their milk production for the year. Over the next six weeks a lot of the cows in the country will have a break from milk production or will be ‘dried-off’. This is when the farmer stops milking the cows. It is the same as what happens on suckler farms when the calf is removed from the cow or weaned.
This is really important as it gives the ‘mammary gland’ the special organ which produces the milk, a chance to rest and repair, before the new calf is born, and the cow begins to produce milk again. The mammary gland is a really cool organ, and it has lots of different names around the country. Some people call it the udder, and others the elder and lots of other names too.
When the cow eats grass and other feeds, the bugs in their stomachs and some special chemicals called enzymes are used to break down that grass and then the cow takes the good parts like amino acids, and energy and fatty acids and minerals and use these to produce milk and help the cow to stay healthy. These nutrients travel around the body in the bloodstream, and when they reach the liver, they are directed to where they are most needed. When the cow is producing milk, a lot of these nutrients are needed in the mammary gland, so that is where the liver sends them. When they arrive at the mammary gland, some of these nutrients are transferred directly into the milk, but others are used to make bigger, more complicated parts of the milk, by special cells in the mammary gland, called secretory cells.

On most farms the cows are milked twice per day. The first milking happens in the morning time, sometimes very early, and then again in the evening. Dairy farmers must milk their cows twice a day, every day, so it is hard work. That’s why lots of dairy farmers really look forward to the break they get when the cows are dried off. But some dairy farmers milk cows all year round (not the same cows for the entire year) and this is where the fresh milk comes from for your breakfast every day!
Read more
Demand and points rise for agricultural science courses
Getting to know the basics of cereals











SHARING OPTIONS